China’s Landmark Achievement: A 1.6% Decline in Carbon Emissions Driven by Clean Energy Growth
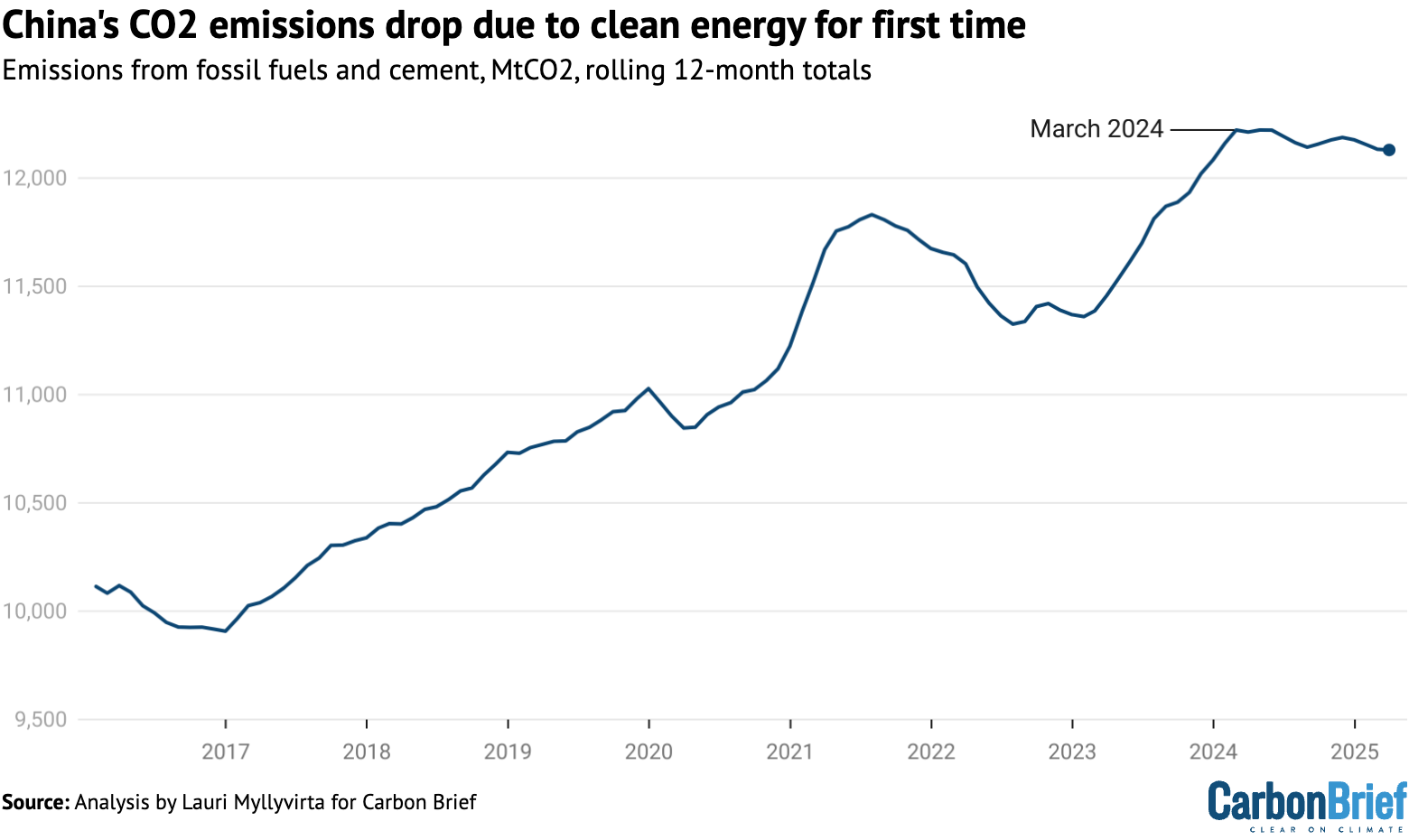
What Happened In the first quarter of 2025, China achieved a 1.6% year-on-year reduction in carbon dioxide (CO₂) emissions, marking the first time that such a decline was driven by an increase in clean energy generation. This achievement occurred despite a 2.
What Happened
In the first quarter of 2025, China achieved a 1.6% year-on-year reduction in carbon dioxide (CO₂) emissions, marking the first time that such a decline was driven by an increase in clean energy generation.
- This achievement occurred despite a 2.5% rise in electricity demand. The reduction was primarily due to a 5.8% drop in power-sector emissions, as renewable sources like wind, solar, and nuclear power expanded rapidly, displacing coal-fired generation .
- In 2024, China added a record 277 gigawatts (GW) of solar capacity and 79 GW of wind capacity, bringing the total installed renewable capacity to over 1,400 GW. Notably, the country’s solar capacity alone surpassed that of the entire United States .
- In a remarkable milestone for environmental sustainability, China has reported a 1.6% decline in carbon emissions, marking a significant step forward in the nation’s fight against climate change. This achievement, driven primarily by rapid expansion in clean energy production and adoption, signals a new era in global climate leadership and highlights the tangible benefits of ambitious renewable energy initiatives.
China, as the world’s largest emitter of carbon dioxide, has faced scrutiny over its environmental footprint. Historically reliant on coal and fossil fuels for economic growth, the country has in recent years embarked on an unprecedented shift toward renewable energy sources, demonstrating that economic development and environmental responsibility can go hand in hand.
The Significance of a 1.6% Emissions Decline
A 1.6% reduction in carbon emissions may appear modest at first glance, but given China’s enormous industrial base and energy consumption, it represents a massive achievement in absolute terms:
- Magnitude: With China contributing over 10 gigatons of CO₂ annually, even a 1.6% reduction equates to millions of tons of emissions avoided.
- Trend Indicator: This marks a positive shift in the long-term trajectory of emissions, suggesting that clean energy adoption is beginning to counterbalance industrial growth.
- Global Impact: As the world’s largest emitter, China’s reduction has a significant effect on global carbon levels, contributing meaningfully to international climate targets.
This milestone is a clear demonstration of the effectiveness of policy, innovation, and investment in reducing emissions, offering optimism for other nations seeking to meet climate goals.
Clean Energy Growth as the Driving Force
The decline in emissions is primarily attributed to the rapid expansion of clean energy sources, including solar, wind, hydropower, and nuclear energy. Several factors have contributed to this growth:
- Investment in Renewable Infrastructure: China has invested heavily in solar farms, wind turbines, and hydropower plants, creating one of the largest clean energy networks in the world.
- Technological Advancements: Improved efficiency and lower costs for renewable energy technologies have accelerated adoption across industries and households.
- Policy Incentives: Government subsidies, tax benefits, and renewable energy quotas encourage companies and local governments to prioritize green energy.
- Transition from Coal: Phasing out or upgrading coal plants with cleaner alternatives has directly reduced carbon emissions from the power sector.
This combination of innovation, policy support, and strategic planning has enabled China to make measurable progress in decarbonizing its energy sector.
Breakdown of Energy Sector Contributions
- Solar Energy: China leads the world in solar panel production and deployment, with millions of rooftops and solar farms generating clean electricity for homes, factories, and public infrastructure.
- Wind Power: Onshore and offshore wind capacity has expanded dramatically, contributing a significant share of the nation’s electricity while displacing fossil fuel usage.
- Hydropower: Existing dams and new projects supply renewable electricity consistently, supporting both urban and rural energy needs.
- Nuclear Energy: Nuclear power plants provide a stable, low-carbon energy source that complements intermittent renewable resources.
Together, these sectors have not only reduced emissions but also strengthened China’s energy security, creating a resilient, diversified energy mix.
Economic and Social Benefits of Emissions Reduction
The decline in carbon emissions carries positive economic and social implications beyond environmental benefits:
- Job Creation: Renewable energy projects have generated millions of jobs in manufacturing, construction, research, and maintenance.
- Health Improvements: Reduced reliance on coal has decreased air pollution, improving public health and lowering healthcare costs associated with respiratory illnesses.
- Technological Leadership: China’s clean energy investments position it as a global leader in renewable technology, opening opportunities for exports and international collaboration.
- Sustainable Growth: Balancing industrial development with emissions reductions demonstrates that economic growth and environmental responsibility are compatible.
These benefits illustrate how addressing climate change can align with broader societal goals, creating a virtuous cycle of growth, health, and sustainability.
Policy Framework and Strategic Vision
China’s success is underpinned by a comprehensive policy framework that promotes clean energy and carbon reduction:
- Nationally Determined Contributions (NDCs): Commitments under the Paris Agreement guide emission reduction targets and renewable energy expansion.
- Carbon Trading Markets: Market mechanisms incentivize companies to reduce emissions, encouraging cost-effective solutions.
- Energy Efficiency Standards: Regulations for industrial, commercial, and residential energy use have improved efficiency, reducing waste and emissions.
- Research and Development Support: Funding for innovation in renewable technologies, smart grids, and storage solutions accelerates progress toward sustainability.
These policies reflect a strategic, long-term vision to transition toward a low-carbon economy while maintaining industrial competitiveness.
Global Implications
China’s 1.6% reduction in carbon emissions is not only a national achievement but also a global milestone:
- Leadership Example: Other countries can learn from China’s integrated approach to policy, technology, and investment.
- Climate Goals Support: Reductions contribute to international efforts to limit global warming and achieve the goals outlined in the Paris Agreement.
- Collaboration Opportunities: As a leader in renewable technology, China can partner with other nations to accelerate global decarbonization.
- Innovation Diffusion: Technological advancements in solar, wind, and energy storage can be shared worldwide, benefiting multiple regions.
This achievement demonstrates how national progress can have far-reaching positive effects on global climate stability and sustainable development.
The Role of Technology and Innovation
Innovation has been a cornerstone of China’s success:
- Smart Grids: Advanced electrical grids optimize energy distribution, integrate renewable sources, and reduce losses.
- Energy Storage: Battery technology and storage solutions stabilize intermittent energy sources like solar and wind.
- AI and Big Data: Monitoring and predictive analytics improve efficiency, reduce waste, and optimize energy consumption.
- Electric Vehicles (EVs): Expansion of EV infrastructure reduces emissions from transportation, complementing clean power generation.
Through these innovations, China demonstrates that technology is a critical enabler of sustainable energy growth and emission reduction.
Positive Public and Industrial Response
The emissions reduction has been met with widespread support from the public, industry, and environmental organizations:
- Corporate Engagement: Many companies are investing in clean energy and sustainable practices to align with national targets and global expectations.
- Public Awareness: Citizens increasingly support renewable energy, energy conservation, and environmentally friendly policies.
- Environmental Advocacy: NGOs and research institutions highlight China’s progress as a success story in global climate action.
This broad engagement underscores that climate action can generate enthusiasm, collaboration, and a shared sense of purpose.
Challenges and Continued Efforts
Despite progress, China recognizes that sustaining and accelerating emissions reduction requires ongoing effort:
- Balancing Industrial Growth: Heavy industries still rely on fossil fuels; transitioning to clean energy must be managed carefully.
- Energy Storage and Grid Integration: Ensuring reliable power supply while incorporating intermittent renewables requires continued innovation.
- International Cooperation: Global climate goals depend on collaborative solutions, knowledge sharing, and cross-border partnerships.
- Public Engagement: Continued education and awareness programs ensure citizens actively support sustainable practices.
By addressing these challenges proactively, China aims to maintain momentum and exceed current reduction levels, setting the stage for long-term climate leadership.
Looking Ahead: The Path to a Low-Carbon Future
China’s achievement demonstrates a clear pathway for sustained emission reductions:
- Expanding Renewable Capacity: Continued investment in solar, wind, and hydro power will further decrease reliance on fossil fuels.
- Energy Efficiency Programs: Improving efficiency across industries and homes reduces emissions while lowering costs.
- Carbon Neutrality Goals: China has committed to achieving carbon neutrality by 2060, with interim targets to ensure steady progress.
- Technological Leadership: Innovation in clean energy, AI, and smart grids will continue to drive reductions and create global impact.
These initiatives showcase a comprehensive, forward-thinking approach to climate action, balancing economic growth with environmental stewardship.
Conclusion: A Positive Milestone for Global Sustainability
China’s 1.6% reduction in carbon emissions marks a landmark achievement in global climate action. Driven by the rapid growth of clean energy, technological innovation, and strategic policy, this milestone demonstrates that even the world’s largest emitter can make tangible progress toward sustainability.
Beyond reducing emissions, the achievement highlights economic, social, and technological benefits, including job creation, improved public health, and global leadership in renewable energy. It serves as an inspiring example for other nations, showing that ambitious goals, combined with policy support and innovation, can lead to meaningful results.
As China continues on its path toward carbon neutrality, this success story provides hope, guidance, and motivation for the global community. It proves that with determination, collaboration, and innovation, a sustainable, low-carbon future is within reach, offering a positive vision for both people and the planet.
China’s proactive approach in expanding renewable energy capacity and reducing carbon emissions demonstrates a significant commitment to environmental sustainability and offers a hopeful outlook for global climate goals.
Explore More Stories of Climate Progress, Clean Energy, and Global Sustainability
If China’s remarkable reduction in carbon emissions inspired you, here are a few more uplifting reads that highlight environmental breakthroughs and collective action shaping a greener future:
- Breakthrough in Clean Energy From Rainwater – A fascinating innovation turning rainfall into a powerful renewable energy source.
- Indonesia’s Waste-to-Energy Revolution: Danantara’s Plan to Turn Trash Into Power – A transformative approach converting waste into clean electricity for communities.
- Uruguay’s Clean Energy Transformation: How a Small Nation Achieved 95% Renewables – A remarkable national success story showing what’s possible with vision and commitment.
Want Daily Encouragement to Stay Hopeful, Eco-Focused, and Inspired?
- Positive Thoughts – Short reminders that keep your mind open and optimistic about global progress.
- Inspirational Words – Motivating lines that spark action, clarity, and purpose.
- Positive Vibes Quotes – Uplifting messages that brighten your day and reinforce environmental hope.
The Positivity Collective
The Positivity Collective is a dedicated group of curators and seekers committed to the art of evidence-based optimism. We believe that perspective is a skill, and our mission is to filter through the noise to bring you the most empowering wisdom for a vibrant life. While we are not clinical professionals, we are lifelong students of human growth, devoted to building this sanctuary for the world.