Spix’s Macaw Returns to the Wild: A Historic Step in Wildlife Conservation
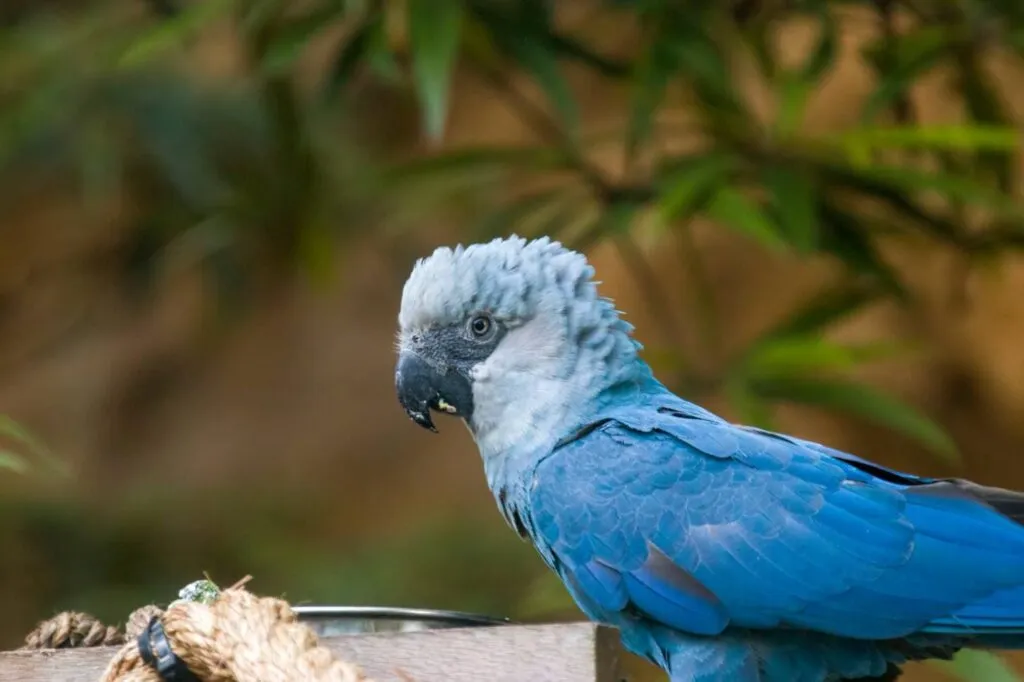
1. What Happened? On January 28, 2025, a significant milestone was achieved in wildlife conservation: 41 Spix's macaws (Cyanopsitta spixii), a species once declared extinct in the wild in 2000, were successfully transported from a breeding facility in Berlin, Germany, to a release center in Bahia, Brazil.
1. What Happened?
On January 28, 2025, a significant milestone was achieved in wildlife conservation: 41 Spix’s macaws (Cyanopsitta spixii), a species once declared extinct in the wild in 2000, were successfully transported from a breeding facility in Berlin, Germany, to a release center in Bahia, Brazil.
Upon arrival, the birds underwent a 28-day quarantine to ensure they were free from diseases that could affect Brazil’s wild ecosystem. The group consisted of 23 females, 15 males, and 3 unsexed juveniles.
Following quarantine, they were integrated into the ongoing reintroduction program in the Caatinga biome, a semi-arid region in northeastern Brazil that is the species’ natural habitat.
- In a landmark achievement for global conservation efforts, the Spix’s Macaw, once considered extinct in the wild, has been successfully reintroduced to its natural habitat in Brazil.
- This historic event marks a triumph for species preservation, international collaboration, and the power of dedicated conservation programs.
- The reintroduction of this vibrant, blue-feathered bird not only signals hope for biodiversity but also underscores humanity’s potential to repair ecosystems that have been degraded over decades.
The return of the Spix’s Macaw, often called the “little blue macaw,” has captured the hearts of conservationists, scientists, and wildlife enthusiasts worldwide. Its story is one of resilience, determination, and the extraordinary impact of coordinated conservation efforts spanning more than two decades.
The Spix’s Macaw: A Symbol of Hope
Native to Brazil’s Caatinga region, the Spix’s Macaw is a medium-sized parrot known for its brilliant blue plumage and gentle temperament. Its story is emblematic of the challenges faced by endangered species:
- Historical Habitat: Spix’s Macaws thrived in the semi-arid forests of Brazil, particularly near riparian areas and specialized nesting trees.
- Threats to Survival: Habitat loss, illegal pet trade, and environmental changes pushed the species to the brink of extinction in the late 20th century.
- Captive Breeding Programs: International conservation efforts, including captive breeding initiatives, became critical to prevent the species’ total disappearance.
- Cultural Significance: Beyond its ecological role, the Spix’s Macaw is a symbol of Brazilian biodiversity and global wildlife preservation.
- Resilience: Its return to the wild demonstrates the power of persistence and human commitment to conservation.
This bird’s story exemplifies the delicate balance between human activity and ecological stewardship, highlighting the responsibility we carry to protect endangered species.
The Conservation Journey
The successful reintroduction of the Spix’s Macaw is the result of decades of careful planning, breeding, and international cooperation:
- Captive Breeding Programs: Zoos and conservation centers worldwide collaborated to breed the species, creating a viable population for reintroduction.
- Habitat Restoration: Teams restored native habitats, planting trees, rehabilitating the landscape, and ensuring suitable nesting areas for the macaws.
- Health and Genetic Monitoring: Advanced veterinary care and genetic studies ensured the birds were healthy, genetically diverse, and ready for survival in the wild.
- Training for Survival: Captive-bred birds were gradually exposed to natural conditions, learning to forage, avoid predators, and navigate their environment.
- Community Engagement: Local communities participated in conservation efforts, fostering stewardship and awareness about protecting the macaw and its habitat.
This comprehensive approach demonstrates that successful species reintroduction requires meticulous planning, science, and community involvement.
International Collaboration and Support
The Spix’s Macaw’s return is a testament to global cooperation in wildlife conservation:
- Partnerships Across Continents: Institutions in Brazil, Europe, and North America shared expertise, funding, and resources to ensure the macaw’s survival.
- Scientific Exchange: Ornithologists, ecologists, and geneticists collaborated to monitor health, breeding, and adaptation strategies.
- Funding and Advocacy: International organizations and governments provided financial and legislative support to safeguard habitats and enforce wildlife protection laws.
- Volunteer Contributions: Volunteers participated in habitat restoration, monitoring, and educational programs, emphasizing the role of community action in global conservation.
- Knowledge Sharing: Lessons learned from the Spix’s Macaw project are now being applied to other endangered species worldwide, amplifying its impact.
This cooperative model highlights that protecting biodiversity is a shared global responsibility and that success often requires unity, dedication, and sustained effort.
Reintroduction to the Wild
The reintroduction process was carefully designed to maximize the macaws’ chances of survival:
- Release Sites: Birds were released into protected areas with abundant food sources, nesting sites, and minimal human disturbance.
- Soft Release Methods: Gradual acclimatization ensured the birds adapted to their environment without shock or stress.
- Monitoring: GPS tracking and field observations allowed conservationists to follow the macaws’ behavior, survival, and adaptation.
- Post-Release Support: Supplemental feeding and veterinary care were available until the birds demonstrated independence.
- Community Collaboration: Local stakeholders were involved in monitoring and protecting the reintroduction sites, promoting sustainable coexistence.
Early reports indicate that the birds are foraging, nesting, and interacting naturally, demonstrating promising signs of successful adaptation.
Ecological Significance
Reintroducing the Spix’s Macaw is not only a victory for the species itself but also strengthens the broader ecosystem:
- Seed Dispersal: Macaws play a role in dispersing seeds, supporting forest regeneration and biodiversity.
- Ecosystem Balance: As part of the food web, their presence supports ecological interactions and stability.
- Indicator Species: The health of Spix’s Macaws reflects the overall condition of their habitat, offering insights for ecosystem management.
- Conservation Awareness: Their return draws attention to the need for preserving semi-arid forests and combating habitat degradation.
- Cultural and Ecotourism Potential: The species attracts nature enthusiasts, fostering eco-friendly tourism and economic benefits for local communities.
By returning to the wild, the Spix’s Macaw contributes to a healthier, more resilient ecosystem, benefiting countless other species and human communities.
Community and Cultural Impact
The reintroduction has had a profound effect on local communities and cultural awareness:
- Educational Programs: Schools and community centers now use the macaw as a living example of conservation success, inspiring youth and local engagement.
- Community Pride: Residents celebrate the return of the bird as a symbol of national and environmental pride.
- Cultural Storytelling: Artists, writers, and media have shared the Spix’s Macaw’s story, spreading awareness about biodiversity and heritage.
- Volunteer Empowerment: Community involvement has strengthened local stewardship and encouraged sustainable practices.
- International Inspiration: The success story motivates other regions and countries to pursue ambitious conservation projects for their endangered species.
This blend of ecological success and social empowerment underscores the holistic benefits of conservation projects.
Scientific Breakthroughs and Innovations
The project achieved success through scientific ingenuity and innovative conservation strategies:
- Genetic Management: Careful breeding strategies ensured genetic diversity, preventing inbreeding and maintaining a healthy population.
- Health Screening: Advanced veterinary care monitored diseases, nutritional needs, and physical condition.
- Behavioral Training: Birds were taught to recognize predators, forage efficiently, and integrate socially.
- Data-Driven Decisions: Monitoring and ecological data informed adaptive management, optimizing release strategies.
- Long-Term Research: Conservationists are studying the macaws to improve reintroduction techniques for other endangered species.
These innovations demonstrate that science and compassion work hand-in-hand to restore endangered species successfully.
Global Recognition and Awards
The Spix’s Macaw’s return has garnered international acclaim:
- Conservation Awards: Multiple organizations have recognized the achievement as a milestone in wildlife protection.
- Media Coverage: Global news outlets have celebrated the species’ reintroduction, spreading awareness and inspiring action.
- Scientific Publications: Studies detailing the project’s methods provide a blueprint for future conservation initiatives.
- Collaborative Recognition: Participating countries, organizations, and volunteers are lauded for their shared dedication and teamwork.
- Public Engagement: The story has captivated social media audiences, raising awareness and funds for ongoing conservation efforts.
Such recognition highlights that success in conservation is both a scientific and societal triumph.
Lessons Learned and Future Prospects
The Spix’s Macaw project offers critical lessons for global conservation:
- Patience and Persistence: Long-term dedication is essential to restore species once considered extinct in the wild.
- International Collaboration: Cross-border partnerships enhance knowledge, resources, and success rates.
- Community Involvement: Engaging local populations ensures sustainable conservation outcomes.
- Adaptive Management: Ongoing monitoring and flexible strategies improve survival and integration.
- Public Awareness: Media, storytelling, and education are crucial to build support for biodiversity initiatives.
Looking ahead, the focus will be on expanding the population, securing habitats, and monitoring ecosystem interactions to ensure the Spix’s Macaw thrives for generations to come.
Conclusion: A Triumph for Nature and Humanity
The reintroduction of the Spix’s Macaw to the wild is a beacon of hope for endangered species worldwide. It demonstrates that with science, collaboration, and unwavering commitment, humans can reverse the decline of even the most critically endangered species.
This success story underscores the importance of biodiversity, habitat restoration, and community engagement. Beyond the ecological impact, it reminds us of the profound effect humans can have when they act with purpose, empathy, and vision.
As the vibrant blue macaws take flight over the Brazilian Caatinga, they carry a message of resilience, hope, and the enduring power of collective action. Their return is not just a win for a single species—it is a victory for nature, science, and the global community, inspiring a new era of wildlife conservation.
The story of the Spix’s Macaw reintroduction serves as a model for conservation success, demonstrating that even the most endangered species can flourish with dedication, knowledge, and cooperation. It is a celebration of life, resilience, and the shared responsibility of humanity to protect our planet’s biodiversity.
Explore More Stories Celebrating Culture, Creativity, and Human Expression
If this article inspired you with its celebration of Black style, artistry, and identity, here are a few more meaningful reads that honor creativity, heritage, and the beauty of self-expression:
- Toni Breidinger: Breaking Barriers as the First Arab-American Woman in Full-Time NASCAR – A powerful story of representation, courage, and redefining who belongs in the spotlight.
- A Kinder World: New Data Shows Compassion Still Trending Up – Evidence that empathy, unity, and social connection are rising globally.
- Maryland Bus Driver Hailed as Hero for Saving Passengers During Fatal Heart Attack – A moving story of bravery that shows everyday people can become heroes in moments of crisis.
Want Daily Encouragement to Stay Inspired, Empowered, and Connected?
- Inspirational Words – Thoughtful lines that spark confidence, ambition, and inner strength.
- Positive Vibes Quotes – Bright, uplifting reminders that fuel optimism and creative energy.
- Encouraging Words – Gentle support to help you stay motivated, courageous, and grounded.
The Positivity Collective
The Positivity Collective is a dedicated group of curators and seekers committed to the art of evidence-based optimism. We believe that perspective is a skill, and our mission is to filter through the noise to bring you the most empowering wisdom for a vibrant life. While we are not clinical professionals, we are lifelong students of human growth, devoted to building this sanctuary for the world.