Japan Builds the World’s First 3D-Printed Train Station
Innovation and technology are constantly reshaping the way we live, travel, and interact with our environment. Japan, a nation long known for its cutting-edge technology and forward-thinking urban planning, has once again captured global attention by building the world’s first 3D-printed train station. This pioneering project is not only a technological marvel but also a symbol of sustainability, efficiency, and creativity, demonstrating how engineering and design can combine to transform infrastructure.
Innovation and technology are constantly reshaping the way we live, travel, and interact with our environment. Japan, a nation long known for its cutting-edge technology and forward-thinking urban planning, has once again captured global attention by building the world’s first 3D-printed train station. This pioneering project is not only a technological marvel but also a symbol of sustainability, efficiency, and creativity, demonstrating how engineering and design can combine to transform infrastructure.
In this article, we explore the design, construction, technology, environmental impact, and societal significance of Japan’s 3D-printed train station, highlighting why this milestone is both inspiring and transformational.
A Vision Turned Reality
The idea of 3D-printing a full-scale train station may have sounded futuristic a few years ago, but in Japan, innovation is often paired with practical solutions. Urban planners, architects, and engineers collaborated to create a structure that is durable, efficient, and visually striking.
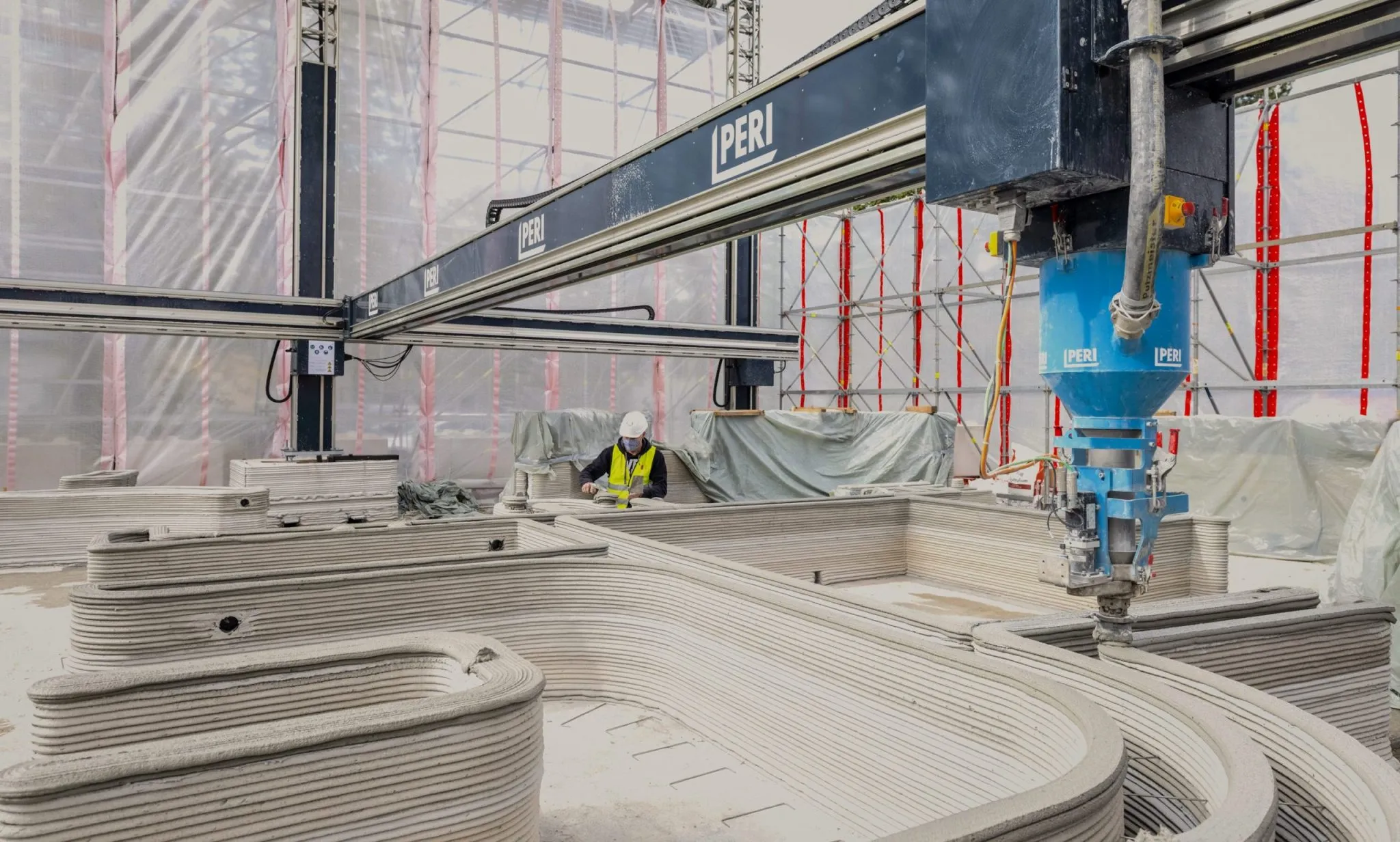
The train station, located in [Insert City/Region], represents a fusion of modern design and functional excellence. Using 3D-printing technology, the team constructed structural components, interior elements, and aesthetic features with remarkable precision. The result is a station that is lightweight yet strong, eco-friendly yet fully functional, and visually engaging for commuters and visitors alike.
The Technology Behind 3D Printing
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, involves layering materials to create three-dimensional structures. Unlike traditional construction, which relies on concrete pouring, scaffolding, and manual assembly, 3D printing allows for:
- Precision Engineering: Complex designs can be fabricated with millimeter accuracy.
- Customization: Unique shapes, curves, and architectural details can be easily integrated.
- Reduced Waste: Materials are added layer by layer, minimizing excess and improving sustainability.
- Faster Construction: Large components can be printed off-site and assembled quickly, reducing labor costs and construction timelines.
For Japan’s train station, advanced 3D-printing techniques allowed the creation of structural panels, benches, ticket booths, and even decorative elements with unmatched efficiency.
Design and Architecture
The station’s architecture reflects Japan’s commitment to blending modernity with accessibility. Designers incorporated features to enhance passenger experience, aesthetics, and functionality:
- Open, Spacious Layout: The station prioritizes passenger flow and comfort, with clear sightlines and intuitive navigation.
- Eco-Friendly Materials: Lightweight, durable materials were used to reduce the environmental footprint.
- Adaptive Design: Modular components allow for easy upgrades, expansions, or customization in the future.
- Integration with Surroundings: The station harmonizes with nearby landscapes and urban environments, creating a welcoming public space.
The combination of 3D printing and thoughtful design results in a station that is both a functional transit hub and a landmark of innovation.
Environmental and Sustainability Benefits
Sustainability was a central consideration in this groundbreaking project. The 3D-printed train station reduces environmental impact in multiple ways:
- Less Material Waste: Traditional construction generates significant waste; additive manufacturing uses only the necessary materials.
- Lower Carbon Footprint: Printing components on-site or nearby minimizes transportation-related emissions.
- Energy Efficiency: The station incorporates energy-saving lighting, ventilation, and insulation systems.
- Longevity: Durable, high-quality materials ensure long-term use, reducing the need for frequent repairs or renovations.
By prioritizing sustainability, Japan demonstrates that advanced technology and environmental responsibility can coexist, setting a new standard for infrastructure worldwide.
Impact on Urban Planning and Public Transportation
The introduction of a 3D-printed train station has significant implications for urban planning and public transportation:
- Rapid Deployment: 3D-printed structures can be deployed faster than traditional stations, addressing growing urban transportation needs efficiently.
- Cost-Effective Expansion: Modular components allow cities to expand transit infrastructure without prohibitive costs.
- Innovation in Design: Designers can experiment with forms and layouts that were previously difficult or expensive to build.
- Accessibility Improvements: Stations can be customized for mobility, safety, and passenger convenience, including ramps, tactile surfaces, and ergonomic seating.
This project signals a shift toward smarter, faster, and more sustainable urban transit solutions, aligning with global trends in technology-driven infrastructure.
The Human Element: Enhancing Commuter Experience
While technology drives the station’s construction, the ultimate goal is improving daily experiences for commuters. Features designed with passengers in mind include:
- Comfortable Waiting Areas: Ergonomic seating, climate control, and natural lighting enhance comfort.
- Clear Signage and Navigation: Easily readable information ensures smooth navigation for both locals and tourists.
- Safety and Security: Integrated safety measures, emergency exits, and surveillance systems enhance security without compromising aesthetics.
- Community Engagement: Public spaces within the station encourage local events, art displays, and community interactions.
The result is a station that not only moves people efficiently but also creates a welcoming environment for connection and engagement.
Global Significance of Japan’s 3D-Printed Station
Japan’s initiative is more than a national achievement; it has global implications:
- Pioneering Technology in Infrastructure: Countries worldwide can learn from Japan’s approach to using additive manufacturing for public spaces.
- Inspiration for Sustainable Design: The project demonstrates how technology can be used responsibly to balance innovation with environmental stewardship.
- Boosting Economic Opportunities: The adoption of 3D-printing technologies can create new industries, jobs, and skill development opportunities.
- Educational Impact: Students, engineers, and architects can study the project as a case study in modern engineering, design, and sustainability.
This milestone positions Japan as a leader in futuristic infrastructure, influencing global trends in construction, urban planning, and transportation.
Community and Cultural Benefits
The station is more than a transit hub—it is a symbol of community progress and cultural pride:
- Local Identity: Architectural elements reflect local culture, creating a station that feels authentic and connected to its surroundings.
- Tourism Boost: Innovative infrastructure attracts visitors, enhancing local economic and cultural engagement.
- Public Engagement: Residents take pride in participating in the unveiling and use of a station that represents forward-thinking design and engineering.
By combining functionality with cultural resonance, the station strengthens the social fabric of the area.
Challenges and Overcoming Them
Like any groundbreaking project, building a 3D-printed train station came with challenges:
- Material Innovation: Engineers had to develop specialized printing materials that were both strong and durable for large-scale construction.
- Precision and Safety: Structural integrity was paramount; rigorous testing ensured the station met all safety and engineering standards.
- Integration with Existing Infrastructure: The new station had to connect seamlessly with rail networks, utilities, and pedestrian pathways.
- Public Acceptance: Educating the public about the benefits and safety of 3D-printed infrastructure was crucial for community support.
By combining technological innovation, rigorous testing, and effective communication, Japan successfully addressed these challenges, paving the way for future projects.
Future of 3D-Printed Infrastructure
Japan’s train station is a glimpse into the future of construction and urban development:
- 3D-Printed Buildings: Future applications may include offices, schools, hospitals, and housing, reducing construction time and cost.
- Customized Urban Spaces: Modular, adaptable designs allow cities to respond quickly to population growth and urban demands.
- Sustainable Cities: Additive manufacturing can significantly reduce environmental impact, supporting green urban initiatives.
- Technological Collaboration: Integration with AI, robotics, and smart materials can create intelligent, adaptive structures.
This project demonstrates that 3D printing is not just a novelty—it is a transformative approach to urban design and sustainability.
Conclusion: A Milestone in Innovation
Japan’s 3D-printed train station represents a remarkable fusion of technology, sustainability, and human-centric design. It is a milestone that:
- Redefines Construction Practices: Demonstrates how additive manufacturing can revolutionize infrastructure.
- Promotes Environmental Responsibility: Reduces material waste, energy consumption, and long-term carbon footprint.
- Enhances Commuter Experience: Provides comfort, accessibility, and community engagement.
- Inspires Global Innovation: Serves as a model for other countries and cities pursuing futuristic infrastructure solutions.
This groundbreaking project embodies the spirit of progress, creativity, and collaboration, reminding us that innovation is not just about what we build—it is about how we build a better, more sustainable future for all.
Japan has once again shown the world that with vision, technology, and commitment, even the most ambitious ideas—like a fully 3D-printed train station—can become reality. As passengers walk through its corridors and experience its modern design, they are witnessing history, celebrating ingenuity, and participating in a journey toward a more innovative and sustainable world.
The world will undoubtedly watch closely as Japan’s pioneering efforts inspire future 3D-printed infrastructure projects across the globe, ushering in a new era of urban development, efficiency, and beauty.
Stay Inspired on Your Innovation & Good News Journey
If this article sparked your curiosity about breakthroughs shaping our world, here are a few more uplifting and forward-thinking stories that highlight humanity’s creativity, progress, and potential:
- Breakthrough in Clean Energy from Rainwater ↗ – Discover how scientists are turning simple rain into a powerful source of renewable energy.
- Spain’s New High-Speed AVE Train Service ↗ – A look at Europe’s newest high-speed upgrade reshaping sustainable travel.
- Toshiba Europe Achieves Long-Distance Quantum Communication ↗ – Explore a groundbreaking leap in secure communication that could transform future technology.
Boost Your Motivation with This Uplifting Resource
Inspirational Words ↗ – A powerful collection of words to spark motivation, hope, and forward momentum in your daily life.
The Positivity Collective
The Positivity Collective is a dedicated group of curators and seekers committed to the art of evidence-based optimism. We believe that perspective is a skill, and our mission is to filter through the noise to bring you the most empowering wisdom for a vibrant life. While we are not clinical professionals, we are lifelong students of human growth, devoted to building this sanctuary for the world.